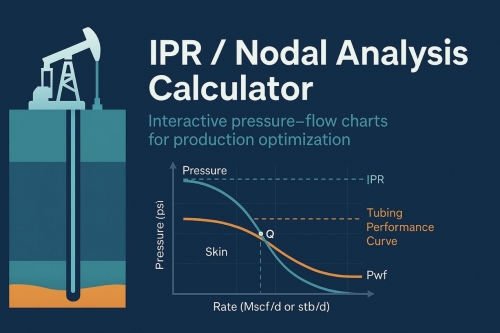
Well testing is the process of measuring and evaluating the productivity and characteristics of an oil or gas well. It is a critical part of the oil and gas industry, as it provides essential information for making informed decisions about well development and management.
Well tests can be conducted at different stages in the life of a well, from exploration to production. During exploration, well tests are used to assess the potential of a reservoir to produce oil or gas. During production, well tests are used to monitor reservoir performance and identify any potential problems.
There are many different types of well tests, each with its own specific purpose. Some of the most common types of well tests include:
- Drill stem tests (DSTs): DSTs are conducted on exploration wells to assess the potential of a reservoir to produce oil or gas. DSTs involve lowering a series of tools into the well to temporarily isolate the reservoir and collect samples of the fluids.
- Production tests: Production tests are conducted on producing wells to monitor reservoir performance and identify any potential problems. Production tests involve flowing the well at different rates and measuring the flow rates and pressures.
- Buildup tests: Buildup tests are conducted on producing wells to measure reservoir pressure and permeability. Builtup tests involve shutting in the well after a production test and measuring the pressure as it builds back up.
Well tests typically involve the use of a variety of equipment, including:
- Wellhead equipment: Wellhead equipment includes valves, chokes, and gauges that are used to control the flow of fluids from the well.
- Separators: Separators are used to separate the oil, gas, and water that is produced from the well.
- Flow meters: Flow meters are used to measure the flow rates of the oil, gas, and water that is produced from the well.
- Pressure gauges: Pressure gauges are used to measure the pressure of the fluids in the well.
The data collected during well tests is analyzed to determine a variety of information about the well and the reservoir, including:
- Reservoir productivity: The productivity of a reservoir is a measure of how much oil or gas it can produce. Well test data can be used to estimate the productivity of a reservoir and to predict its future production performance.
- Reservoir pressure: The pressure of a reservoir is a critical factor in determining its productivity. Well test data can be used to measure reservoir pressure and to monitor changes in pressure over time.
- Reservoir permeability: The permeability of a reservoir is a measure of how easily fluids can flow through it. Well test data can be used to estimate the permeability of a reservoir and to identify any potential damage to the formation.
Well test data is also used to calibrate reservoir simulators. Reservoir simulators are computer models that are used to predict the behavior of reservoirs over time. By calibrating reservoir simulators with well test data, engineers can make more accurate predictions about reservoir performance and optimize well production.
Well testing is a complex and challenging operation, but it is essential for the safe and efficient production of oil and gas. Well test data provides engineers and geologists with the information they need to make informed decisions about well development and management.

%20(1).png)