The oil and gas industry is a complex network of processes, each with its own specific role in bringing hydrocarbons from their source to end-users. One crucial part of this industry that often goes unnoticed by the general public is the midstream sector. In this article, we'll explore what midstream oil and gas is, its significance, and its role in the energy supply chain.
Understanding the Energy Supply Chain
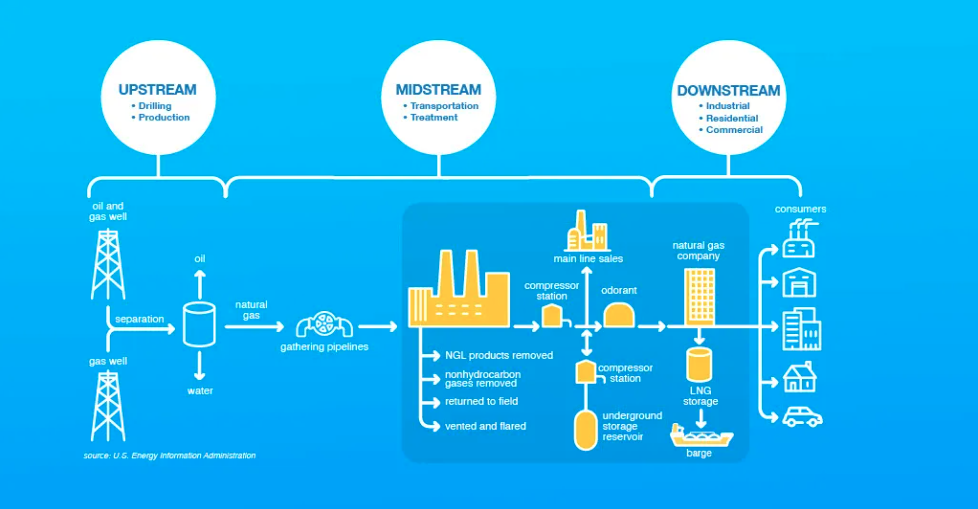
Before delving into midstream operations, it's essential to understand the energy supply chain. It consists of three primary sectors:
Upstream: This sector involves the exploration and production of oil and natural gas. It includes activities such as drilling wells, extracting hydrocarbons, and initial processing.
Midstream: The midstream sector acts as the bridge between the upstream and downstream sectors. It focuses on the transportation, storage, and wholesale marketing of crude oil, natural gas, and natural gas liquids (NGLs).
Downstream: The downstream sector encompasses refining, processing, and distributing petroleum products to end-users. This includes gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, and various petrochemicals.
Now, let's explore the midstream sector in more detail.
What Is Midstream Oil and Gas?
Midstream oil and gas refer to the stage of the energy supply chain that deals with the transportation and storage of raw hydrocarbons. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring that these resources reach their intended destinations safely, efficiently, and in the right quantities.
Key Components of Midstream Operations:
Transportation: The midstream sector includes pipelines, trucks, rail, and ships used to move crude oil, natural gas, and NGLs from production sites to processing facilities or distribution points. Pipelines are a particularly vital component, covering vast distances and ensuring a steady flow of resources.
Storage: Midstream companies operate storage facilities such as tanks, caverns, and terminals to store hydrocarbons temporarily. This storage capacity helps stabilize supply during fluctuations in demand and ensures that reserves are available when needed.
Processing: Some midstream operations involve initial processing of raw resources, such as separating NGLs from natural gas. This processing enhances the quality and marketability of the products.
Wholesale Marketing: Midstream companies also engage in the wholesale marketing of hydrocarbons, negotiating sales and contracts with downstream businesses, such as refineries and petrochemical plants.
Significance of Midstream Operations:
Reliable Energy Supply: Midstream operations are critical for maintaining a consistent and reliable supply of energy resources to consumers. Any disruption in this sector can affect energy prices and availability.
Economic Impact: The midstream sector contributes significantly to the economy by creating jobs, generating revenue, and supporting related industries.
Environmental Considerations: Midstream companies are increasingly focused on environmentally responsible practices, including the prevention of spills, emissions reduction, and pipeline integrity management.
Global Energy Trade: Midstream facilities facilitate the international trade of oil and gas, connecting producers with consumers around the world and shaping global energy markets.
Conclusion
In the intricate web of the oil and gas industry, the midstream sector plays a pivotal role in ensuring that hydrocarbons travel safely and efficiently from production sites to end-users. It forms a crucial link between the upstream and downstream sectors, contributing to a reliable and accessible energy supply. As the industry continues to evolve, midstream operations will remain essential for meeting the world's energy needs while addressing environmental and logistical challenges.

%20(1).png)