Tool joint drill pipe is an essential part of the drill string, which is a series of connected pipes and components used to transmit drilling fluid and rotational force to the drill bit. The drill bit is responsible for creating boreholes in the Earth's subsurface. The tool joint drill pipe plays a vital role in the drilling process by connecting the surface drilling equipment to the drill bit and transmitting torque and axial load.
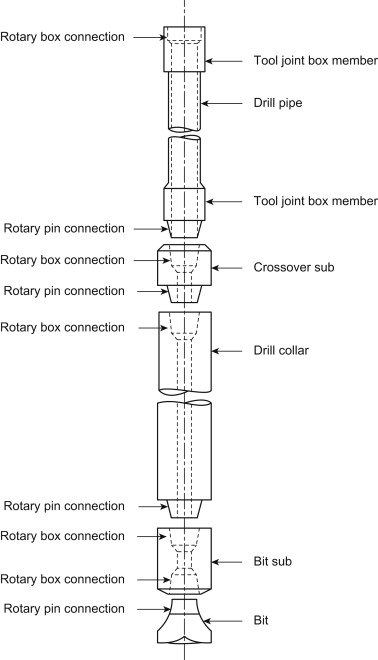
Construction and Components:
Tool joint drill pipe is typically constructed from high-strength steel to withstand the extreme conditions encountered during drilling. It consists of several key components:
Pipe Body: The main body of the drill pipe is a cylindrical steel tube with a threaded connection on each end. The pipe body is designed to withstand high levels of stress, bending, and torsional forces.
Tool Joints: Tool joints are thickened sections located at both ends of the pipe body. These sections are specially designed with threading and shoulders that facilitate secure connections between individual drill pipes. The tool joints also endure the most stress during drilling operations.
Threaded Connections: The threaded connections of the tool joint drill pipe allow for easy assembly and disassembly of the drill string. These connections ensure a tight seal to prevent fluid leakage and maintain drilling efficiency.
Internal Bore: The internal bore of the drill pipe provides a pathway for drilling mud to flow from the surface to the drill bit. Drilling mud serves several purposes, including cooling the drill bit, carrying cuttings to the surface, and maintaining pressure in the borehole.
Role in Enhancing Drilling Operations:
The tool joint drill pipe offers several benefits that contribute to the overall efficiency and success of drilling operations:
Durability: Due to its robust construction, the tool joint drill pipe can withstand the demanding conditions of drilling, including high pressures, vibrations, and extreme temperatures.
Torque Transmission: The tool joint drill pipe efficiently transmits torque from the surface equipment to the drill bit. This torque is essential for the rotation of the drill bit and the creation of boreholes.
Axial Load Transmission: Along with torque, the tool joint drill pipe transmits axial load, allowing the drill bit to apply downward force for efficient drilling.
Connection Integrity: The threaded connections and tool joints ensure a secure link between the drill pipes, minimizing the risk of component separation during drilling.
Drilling Fluid Circulation: The internal bore of the drill pipe enables the circulation of drilling mud, which aids in cooling and lubricating the drill bit, carrying cuttings to the surface, and maintaining stability in the borehole.
In conclusion, the tool joint drill pipe is an indispensable component of drilling operations across various industries. Its construction, featuring durable materials and specialized design, allows for efficient torque and axial load transmission, connection integrity, and drilling fluid circulation. By enabling these essential functions, the tool joint drill pipe plays a pivotal role in enhancing drilling efficiency, safety, and overall project success.

%20(1).png)