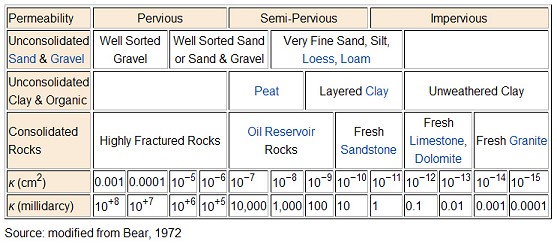
Permeability is a measure of a rocks ability to transmit fluids. In addition to being porous, a reservoir rock must allow fluids to flow through its pore network at practical rates under reasonable pressure differentials.
Controls on permeability include:
• The size of the available pores.
• The connecting passages between the pores.
Absolute Permeability - The ability to transmit a fluid when 100% saturated with one fluid.
Effective Permeability - The ability to transmit a fluid in the presence of another fluid when the two are immiscible.
Relative Permeability - Ratio of effective to absolute.
Permeability, as a darcy, is defined as:
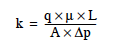
where: q = 1 cc/s (volumetric rate of fluid flow)
A = 1 cm2 (cross-sectional area)
m = 1 centipoise (viscosity of flowing fluid)
Dp/L = 1 atmosphere/cm (pressure gradient)
A permeability of one darcy is usually much higher than that commonly found; consequently, a more common unit is the millidarcy, where:
1 darcy = 1000 millidarcy's
A practical oil field rule of thumb for classifying permeability is:
poor to fair = 1.0 to 15 md
moderate = 15 to 50 md
good = 50 to 250 md
very good = 250 to 1000 md
excellent = 1 darcy
Besides the typical matrix permeability, some reservoir rocks may have solution channels, vugs, or fracture systems which will increase permeability.
Permeability of solution channels is directly related to the size of the channels;
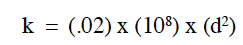
where: d = diameter of the channel, (in.)
Permeability of fractures is a direct function of the fracture width:
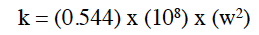
where: w = width of fraction, (in.)
Reservoir permeability is a directional property. Horizontal permeability (kH) is measured parallel to bedding planes. Vertical permeability (kV) across bedding planes is usually lower than horizontal. The ratio kH/kV normally ranges from 1.5 to 3.
When only a single fluid flows through the rock, the term absolute permeability is used. However, since petroleum reservoirs contain gas and/ or oil and water, the effective permeability for given fluids in the presence of others must be considered. It should be noted that the sum of effective permeabilities will always be less than the absolute permeability. This is due to the mutual interference of the several flowing fluids.
Reservoir Permeability from Log Data
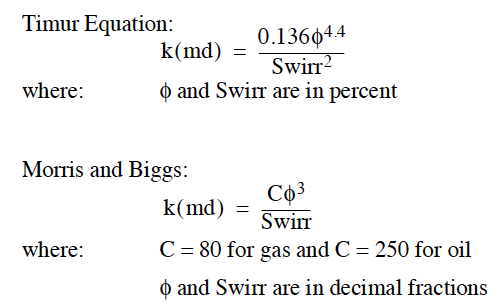

%20(1).png)